Flexibility, often overshadowed by strength and endurance, plays a crucial role in overall fitness and well-being. While stretching and mobility exercises are commonly associated with improving flexibility, the impact of diet on this aspect of fitness is often overlooked. However, emerging research suggests that what we eat can significantly influence our flexibility levels. In this article, we delve into the intricate relationship between diet and flexibility, uncovering the nutrients and dietary practices that can enhance or hinder our body’s ability to move freely.
The Role of Nutrients in Flexibility
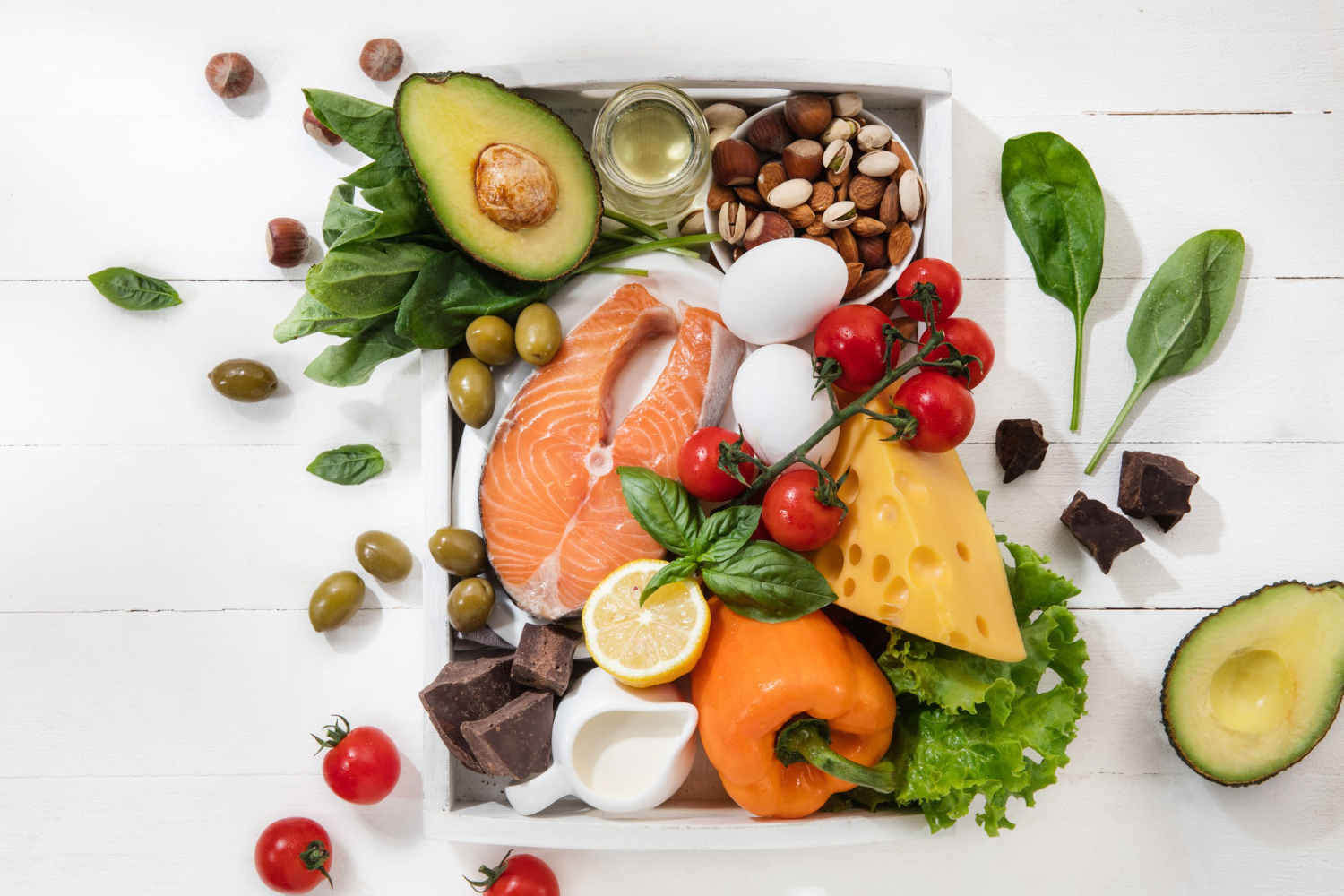
- Hydration: Adequate hydration is fundamental for maintaining optimal flexibility. Water acts as a lubricant for joints and facilitates the flow of nutrients to muscles, aiding in their flexibility and range of motion. Dehydration, on the other hand, can lead to stiffness and decreased elasticity in muscles and connective tissues. Ensure you’re drinking enough water throughout the day to keep your body hydrated and your muscles supple.
- Protein: Proteins are the building blocks of muscles, tendons, and ligaments, all of which contribute to flexibility. Consuming an adequate amount of high-quality protein sources supports muscle repair and growth, enhancing flexibility and reducing the risk of injury. Incorporate lean proteins such as chicken, fish, tofu, and legumes into your diet to promote muscle elasticity and overall flexibility.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Found in fatty fish, flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts, omega-3 fatty acids possess anti-inflammatory properties that can alleviate joint stiffness and improve flexibility. Including these foods in your diet can help reduce inflammation in the body, allowing for greater mobility and ease of movement.
- Antioxidants: Antioxidant-rich foods such as fruits, vegetables, and green tea help combat oxidative stress and inflammation, both of which can impair flexibility. By neutralizing free radicals and supporting tissue repair, antioxidants promote healthy joints and muscles, enhancing flexibility and mobility.
Dietary Practices for Optimal Flexibility
- Balanced Macronutrient Intake: A well-rounded diet that includes a balance of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats provides the energy and nutrients necessary for optimal muscle function and flexibility. Avoid restrictive diets that deprive your body of essential nutrients, as they can compromise muscle health and hinder flexibility.
- Pre- and Post-Workout Nutrition: Fueling your body with the right nutrients before and after exercise is crucial for maximizing flexibility gains and minimizing muscle stiffness. Consume a combination of carbohydrates and protein before your workout to provide energy and support muscle repair. After exercise, replenish lost fluids and nutrients with a nutritious meal or snack containing protein, carbohydrates, and healthy fats.
- Incorporate Anti-Inflammatory Foods: Incorporating anti-inflammatory foods into your diet can help reduce inflammation in the body, promoting flexibility and joint health. Include foods such as turmeric, ginger, berries, leafy greens, and nuts in your meals to support overall flexibility and mobility.
- Stay Consistent and Patient: Improving flexibility through diet takes time and consistency. Be patient with yourself and focus on making sustainable dietary changes that support your long-term health and fitness goals. Incorporate nutrient-rich foods into your meals, stay hydrated, and prioritize recovery to optimize flexibility and mobility over time.
In conclusion, diet plays a significant role in influencing flexibility and overall mobility. By prioritizing hydration, consuming adequate protein, incorporating omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants, and following sound dietary practices, you can support your body’s ability to move freely and prevent stiffness and injury. Remember that flexibility is a key component of fitness and well-being, and by nourishing your body with the right nutrients, you can enhance your flexibility and enjoy the benefits of improved mobility in your daily life. Embrace a balanced diet rich in whole, nutrient-dense foods, and reap the rewards of a more flexible and agile body.